
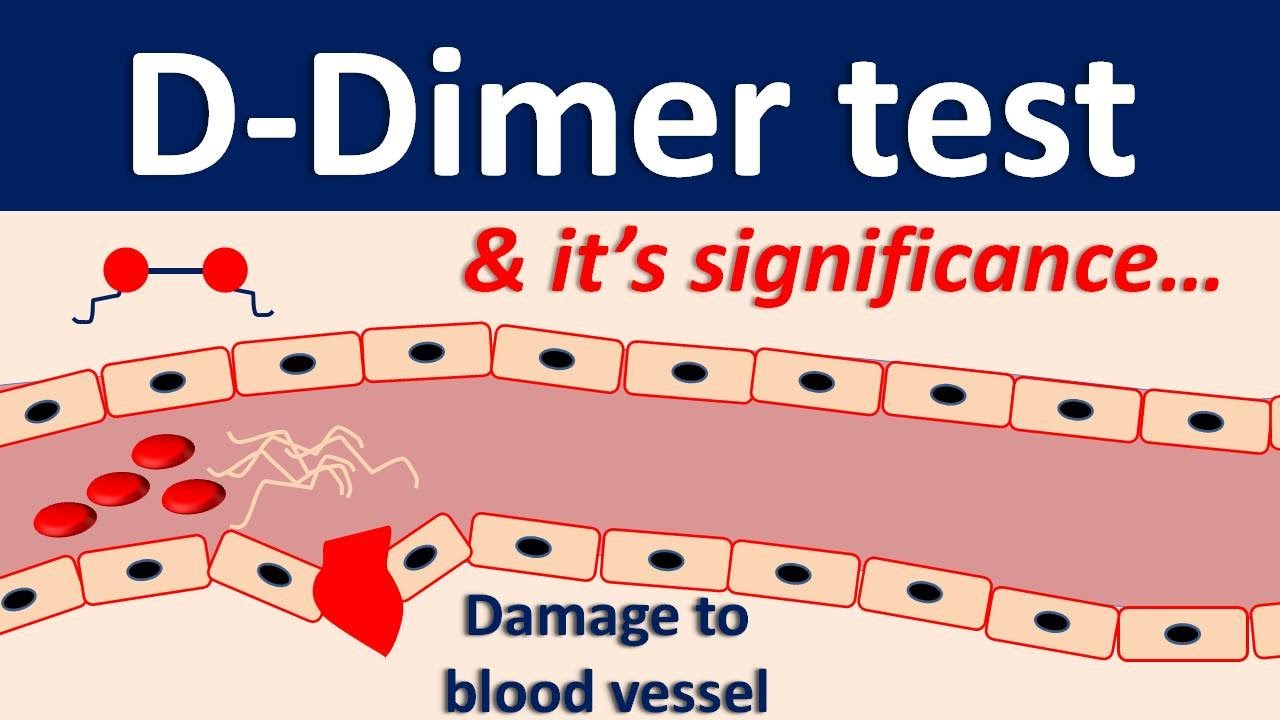
Increased concentration of D-Dimer may also be observed in the elderly or hospitalized patients with abnormal coagulation caused by bacteremia

Myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, pulmonary embolism, venous thrombosis, surgery, cancer, disseminated intravascular coagulation, infection and tissue necrosis may lead to elevated concentration of D-Dimer.
Clinical Utility: D-Dimer <0.50 mcg/mL can be used to rule out DVT/PE in >98 outpatients with low clinical probability.Test also performed by the Rapid Response Lab. Diazymes D-Dimer Assay is for the quantitative determination of fibrinogen/fibrin degradation products (D-Dimer) in human plasma. D-DIMER, QUANTITATIVE Contraction, - UAB Procedure Number, 2500116 CPT Code, 85379 Specimen, Collect one (1) blue-stopper tube (3.2 sodium citrate). May be tested from same tube as PTT however, follow PTT stricter collection and delivery guidelines. In addition, D-Dimer is used in the diagnosis of blood disorders disseminated by intravascular coagulation. D-Dimer has increased specificity and is performed instead of FSP/FDP. A positive result can indicate thrombosis but does not rule out other potential causes. A D-dimer result is more likely to be a false-positive in a person over age 50. If testing was performed only once, or very infrequently. This study has numerous weaknesses: Its unclear how frequently DVT studies were performed. The best cutoff was 1,500 ng/ml (with a sensitivity of 85 and a specificity of 89). I learned this firsthand with my mother’s ER visits. The authors subsequently tested various D-dimer cutoff values for the ability to predict DVT occurrence. Therefore, D-Dimer is commonly used to exclude thromboembolic disease where the probability is low. The D-dimer blood test is to screen for a blood clot, and doctors routinely order this test when a patient presents to an ER with symptoms that a blood clot in the lung can cause. D-Dimer is not normally present in human blood, except when the coagulation system has been activated, for instance because of the presence of thrombosis or disseminated intravascular coagulation. The D-Dimer Chemiluminescence ImmunoAssay (CLIA) Test is a chemiluminescence-based immunoassay for the quantitative detection of DDimer in human plasma (Lithium heparin, EDTA, citrate) or whole blood using the ALTA CLIA lyzer.ĭ-Dimer is the fibrinolysis-specific degradation product found in human blood.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
